To get an ADSL broadband connection, first, you need to check the availability of BT lines in your area. Second, you would choose your ADSL broadband internet provider and check the availability of that service provider in your area.
To check the availability of ADSL broadband providers in UK, visit samknows.com/broadband. It is an excellent broadband information site providing map, coverage details of all UK ADSL providers.
You will be asked to enter your telephone number or the postcode of your area. You will then get the list of ADSL providers who offer broadband service in your area. Just pick the service you think suitable for you.
Why is ADSL the most popular broadband type in UK?
- Excellent availability. Most areas in UK are connected by BT lines and any household or business in UK can get an ADSL broadband connection now. (99 % coverage in UK)
- ADSL broadband is more than 10 times faster than a dial-up service. Unless you are too away from the local exchange or your line is noisy, you will get reasonably good speeds depending on the package.
- ADSL broadband is a newer technology (when comparing to dial-up) that allows you to get home phone and broadband services on the same line. It can save your family spend on telecom services.
- ADSL is a fixed line broadband that is suitable for heavy users. ADSL broadband providers offer excellent monthly download limits that can meet your needs within the cost you have planned. You may also choose unlimited ADSL broadband packages which allow you to download as much as you like.
- With ADSL broadband, you can also add some innovations like wired or wireless networking and your entire family can share single broadband connection.
How ADSL broadband works?
Say, you have signed up with your ADSL broadband provider. Your provider will immediately supply you with a broadband installation kit that includes filter, installation CD, a few cables, an ADSL modem or router.
If you do not have BT phone lines, order and get it. That may take a few days but you need to wait anyhow. After getting BT lines, choose the ADSL broadband service.
If you have BT phone lines already, the installation of ADSL broadband would not take much time.
- Installation CD will help you to configure your ADSL broadband modem or router.
- Cables will connect your PC, modem, filter and BT phone socket.
- Filter divides the telephone wire so that both voice and data can be transmitted simultaneously. It helps us to use telephone while we will be surfing the net.
How can telephone wires bring you broadband?
In your local BT exchange, your provider installs a device that allows the same copper wire to carry both voice and data signals in two channels. One channel uses the frequency range of 0 – 20 KHz for voice communication while the other channel uses higher frequency range of 26 KHz – 1 Mhz for transmiting data at faster speed.
At home, you need an ADSL filter to split the two signals and get two services together – homephone and broadband. You will connect the phone plug into the slot marked ‘phone’ in the filter while data cable from the modem or router will be connected to other slot marked ‘modem’. Using a router, you can connect more than a computer to an ADSL router to share a single broadband connection.
What speeds that ADSL broadband users in UK get?
In the current scenerio, UK broadband users have three major options to choose – ADSL, cable and mobile. How these technologies fare, when it comes to delivering speeds?
The recent broadband speed report from Ofcom, UK telecom regulator shows that speeds signficantly vary depending upon the technology and the capacity of the provider’s network.
The following table shows the results of nationwide speed tests conducted on UK’s major ADSL broadband providers network conducted by Ofcom and Samknows between November 2008 and April 2009. While the average broadband speed was found to be 4.1 megabits per second (Mbit/s), Virgin Media cable, the fastest ISP, found outperforming all UK ADSL providers in the list.
| Broadband ISP | Connection Speed | Average speed |
| AOL Broadband | 8Mbps | 3.3 to 3.9Mbps |
| BT | 8Mbps | 3.8 to 4.2Mbps |
| O2 | 8Mbps | 4.1 to 5.1Mbps |
| Orange | 8Mbps | 3.8 to 4.5Mbps |
| Plusnet | 8Mbps | 3.8 to 4.9Mbps |
| Sky | 8Mbps | 4.0 to 4.7Mbps |
| TalkTalk | 8Mbps | 3.8 to 4.6Mbps |
| Tiscali | 8Mbps | 3.2 to 3.7Mbps |
| Virgin Media (cable) | 10Mbps | 8.1 to 8.7Mbps |
ADSL broadband availability in UK
There are over 5444 ADSL enabled exchanges (BT wholesale), 5438 ADSL Max enabled exchanges, 809 SDSL enabled exchanges and 573 WBC enabled exchanges (BT wholesale) in the UK. Just visit samknows.com/broadband and enter your village/town name, postcode, phone number or exchange code to check the availability of providers in your area.
Following maps from Samknows show 5514 ADSL enabled exchanges and 747 SDSL enabled exchanges in UK (marked with green). You may also find more coverage maps, especially of ADSL 2+ providers like Be, O2 etc.
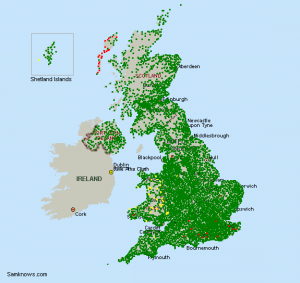
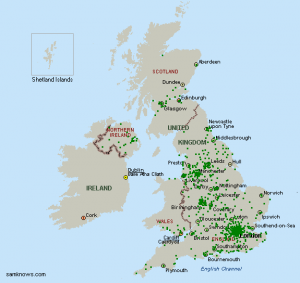
Types of ADSL Broadband
Digital Subscriber Line or DSL is a way of connecting to broadband internet using (copper) telephone wires. There are mainly two types of DSL connectivity – Asymmetric and Symmetric.
Both Asymmetric and Symmetric DSL technologies have sub-types:
Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line (ADSL) Technology
Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line (ADSL) provides more downstream bandwidth. Bandwidth refers to the amount of data that can be transferred across the line. Downstream refers to data transferred to the user’s computer. Upstream bandwidth on ADSL can be one tenth of downstream bandwidth. For instance, if you get 4 – 5 Mbps download speed, it is more likely that you will get uploads speeds around 350 Kbps.
Typical download speeds can be ranging between 384Kbps and 6Mbps on 8Mbps ADSL broadband line. Average upload speed on a 8Mbps line can be upto 1.5Mbps.
ADSL is currently the most common DSL technology, especially with home users, for a simple reason that most internet applications require more downstream bandwidth like surfing, downloading files, accessing streaming contents such as music or video clips etc.
ADSL 2 and ADSL 2+
ADSL 2 and ADSL 2+ can provide higher speeds (up to 24Mbps) than ADSL. However, maximum speeds you will get, depend on the distance from the exchange. (within 1 km radius, you get excellent speeds).
Very high bit-rate DSL (VDSL)
As the name indicates, this ADSL transfers data at very high speeds. VDSL can provide download speed up to 100Mbps, however, over short distances (only up to 350m from the central office/cabinet). VDSL speeds drop drastically over long distances. It is a developing technology.
DSL Lite
In this ADSL version, the DSL splitter is placed at the exchange, instead of user’s place. Speeds are limited.
Rate Adaptive DSL (RADSL)
This ADSL connectivity enables the users to adjust the connection speeds with respect to line quality and distance from the exchange. Software is used for this purpose.
Symmetric Digital Subscriber Line (SDSL)
Symmetric Digital Subscriber Line (SDSL) is not as common as ADSL. It provides equal amount of bandwidth in both upstreams and downstreams. SDSL is mostly used by businesses which need to send and receive large amounts of data, files etc. You may get SDSL services with business ISPs.
SDSL or single line DSL
It is the standard version of symmetric DSL broadband and used widely in businesses. It is also known as Single-pair high-speed Digital Subscriber Line (G.SHDSL).
Speeds are symmetric, slower than standard ADSL (8Mbps), but higher upload speeds (up to 4.5Mbps) can be achieved by using two pair line.
High bit-rate DSL (HDSL)
HDSL provider faster connection speeds than normal SDSL connection, but not used for home broadband connectivity. This technology has been going through improvements over the time.
VDSL 2
This symmetric DSL connection can provide both upload and down speeds up to 100Mbps over excellent distance range, however, it is too expensive so the rate of adoption is naturally slow.